Biology has a “rendering” problem.
For 50 years, the central dogma of drug discovery was “lock and key.” If one wants to cure a disease, one must find the protein responsible (the lock) and design a molecule that fits perfectly into it (the key). The problem? The “lock” is microscopic, wobbly, and invisible. Finding the key was a game of blind chemistry, costing roughly $2 billion and 10 years per drug.
In 2024, Google DeepMind released AlphaFold 3. It didn’t just solve the protein folding problem (again); it solved the interaction problem.
This marks the shift from “Static Biology” to “Dynamic Biology.” And it is going to crash the cost of drug discovery.
From Evoformer to Diffusion: The Architecture Shift
To understand why AlphaFold 3 (AF3) is a quantum leap over AlphaFold 2 (AF2), one must look at the engine.
AlphaFold 2 relied on the Evoformer architecture. It was an “attention-heavy” model that looked at evolutionary history (Multiple Sequence Alignments, or MSAs) to triangulate where atoms should be. It was brilliant at predicting static protein structures. If you gave it a sequence, it gave you a shape. But it was rigid.
AlphaFold 3 throws much of that away. Instead, it uses a Diffusion Network, similar to the AI models that generate images (like Midjourney or Stable Diffusion).
How Biological Diffusion Works
Imagine a protein structure as a sharp, clear image.
- Forward Process (Noise): You slowly add static (Gaussian noise) to the coordinates of every atom until the molecule looks like a cloud of random chaos.
- Reverse Process (Denoise): You train an AI to look at that chaos and “hallucinate” the structure back into existence, step by step.
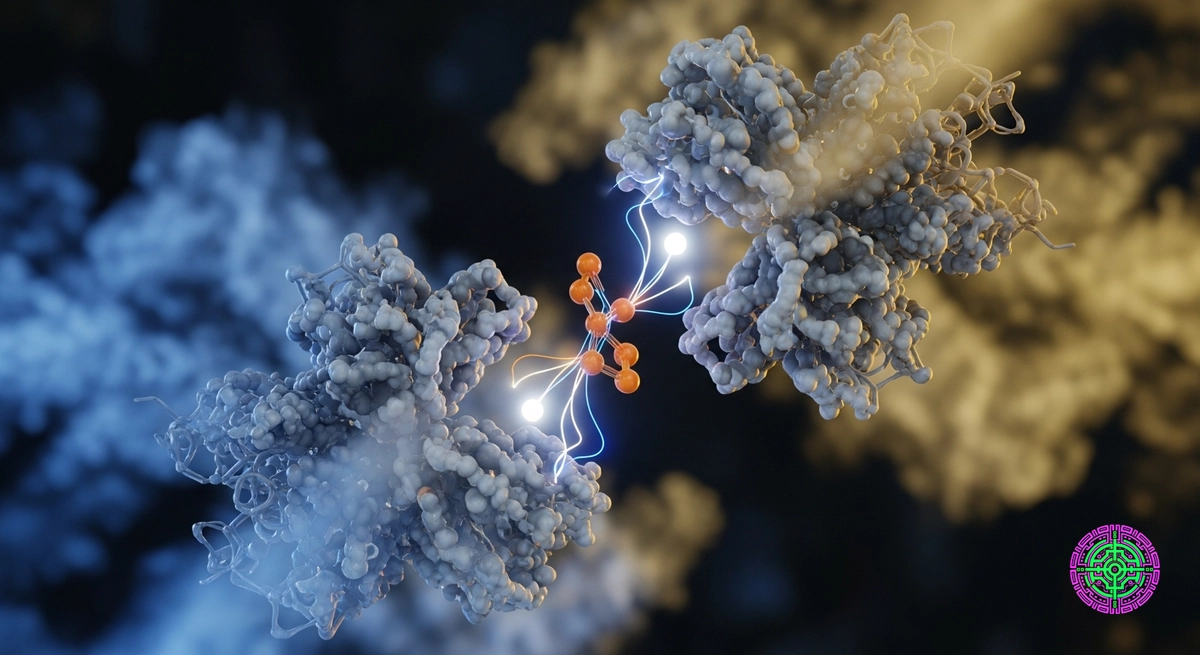
AF3 takes a cloud of random atoms and “denoises” them into a perfectly folded protein-ligand complex. This allows it to handle generative uncertainty. Unlike AF2, which output a single static answer, AF3 understands that molecules are flexible. They breathe.
The Pairformer Module: Reducing MSA Dependence
One of the critical weaknesses of AlphaFold 2 was its heavy reliance on Multiple Sequence Alignments (MSAs). It needed to see thousands of “cousin” proteins across evolutionary history to figure out the shape of the target. This meant it failed on “orphan proteins” (proteins with no known relatives) or synthetic antibodies.
AlphaFold 3 introduces the Pairformer module. This updated attention mechanism processes the chemical constraints of the atoms themselves rather than just their evolutionary history. It focuses on the “pairwise” relationships between atoms—basically, the laws of physics and chemistry (Van der Waals forces, electrostatics).
This shift makes AF3 significantly better at predicting antibody-antigen interactions, a domain where evolutionary data is often sparse or irrelevant.
The “Everything” Machine
The limitation of AlphaFold 2 was that it only spoke “Protein.” But biology is multilingual.
- DNA/RNA: The instruction code.
- Ligands: Small molecules (drugs) that bind to proteins.
- Ions: Charged particles (Zinc, Magnesium) that act as batteries or switches.
- Post-Translational Modifications: Calculating how phosphorylation changes a protein’s shape.
AF3 is the first unified model. It predicts the structure of complexes including proteins, nucleic acids, small molecules, ions, and modified residues.
The Drug Discovery Impact
This is the “Holy Grail” for Pharma. Most drugs act by binding a small molecule (ligand) to a protein. AF2 could tell you what the protein looked like, but it couldn’t tell you if your drug would stick to it. AF3 can.
Benchmarks show a 50% improvement in accuracy for protein-ligand interactions over traditional physics-based docking software (like energetic docking). This effectively replaces wet-lab crystallography for the initial screening phase. Instead of testing 10,000 compounds in a physical lab, researchers can screen 10 million compounds in a server ranch.
Confidence Metrics: Determining Truth vs. Hallucination
In a diffusion model, hallucination is a feature, not a bug. To combat this, AF3 outputs confidence scores that are just as important as the structure itself.
- pLDDT (Predicted Local Distance Difference Test): This 0-100 score measures local confidence. If a region has a low pLDDT (<50), it likely means that region is intrinsically disordered (floppy) in real life, not just that the model is confused.
- PAE (Predicted Aligned Error): This measures the error between different domains. It answers: “Is shape A correct, and is shape B correct? More importantly, is the attachment point between them valid?”
Pharma companies use these metrics to “filter” the generative output. If AF3 predicts a drug binds with high confidence (low PAE), it moves to the wet lab. If confidence is low, it is discarded.
Isomorphic Labs: The $100 Billion Bet
Google isn’t just giving this away for free. They spun out Isomorphic Labs (led by Demis Hassabis) to commercialize it.
Their strategy is “AI-First Drug Design.” Instead of licensing the tool to Pfizer (though they have partnerships with Eli Lilly and Novartis), Isomorphic acts as a “Digital Biotech.” They identify targets, design drugs in silico using AF3, and then sell the molecule itself to Pharma partners for billions.
The Model: “The shovel is not for sale. The gold is found, the mine is mapped, and the GPS coordinates are sold.”
By keeping the most advanced version of AF3 proprietary (or available only via a restricted server), Isomorphic maintains a massive competitive moat.
The Competitive Landscape: It’s Not Just Google
While Google grabbed the headlines, the field is moving fast.
- Chai-1: released by Chai Discovery, this open-weights model claims to match or beat AF3 on certain ligand-binding benchmarks. It runs on consumer hardware.
- ESM3 (Evolutionary Scale Modeling): Built by EvolutionaryScale (ex-Meta researchers), this is a “Foundation Model for Biology.” It generates new proteins from scratch rather than just folding existing ones.
- BioNeMo: NVIDIA’s framework effectively wraps these models into an enterprise-grade service, becoming the “AWS of Biology.”
The monopoly on digital biology lasted about six months. Now, it is an arms race. A key dynamic to watch is the tension between Open Science and Commercial Moats. While DeepMind published the methods for AlphaFold 3, they initially withheld the code and weights, breaking from their precedent with AlphaFold 2. This sparked a backlash from the scientific community, eventually leading to a partial release.
This friction highlights the commercial value of these models. In 2021, protein folding was a scientific curiosity. In 2025, it is a trade secret worth protecting with the same vigor as the Coca-Cola formula. The appearance of competent open-source rivals like Chai-1 suggests that the algorithmic “moat” may be shallower than Google hopes, forcing Isomorphic Labs to compete on proprietary data (the wet lab loop) rather than just model architecture.
The Data Gap: Why Wet Labs Survive
Despite the hype, AlphaFold 3 is not a magic wand. It suffers from the “garbage in, garbage out” problem.
- Hallucinations: Like ChatGPT, AF3 can confidently predict a structure that defies physics (e.g., atoms overlapping or unnatural bond angles). A “diffusion” model is prone to making things look plausible rather than real.
- Dynamics: It predicts a “snapshot” of a molecule. But proteins optimize between different shapes (conformations). AF3 often misses these “hidden” states which are crucial for drug binding (allosteric sites).
This means wet labs aren’t dead. They just change function. Instead of discovery, labs are now for verification.
The 2026 Outlook: Generative Biology
The industry is entering the era of Generative Biology.
Just as GPT-4 can write code, AlphaFold 3 generates biological hypotheses. The next step (AlphaFold 4?) will likely close the loop: not just predicting structure, but predicting function. “Design a protein that eats plastic” or “Design a binder that neutralizes Spike Protein variant X.”
When that happens, biology stops being a science of discovery and becomes a science of engineering. The code of life becomes, literally, code.



🦋 Discussion on Bluesky
Discuss on Bluesky